Since oxidative stress became the classic theory of cellular aging, finding safe, efficient, and multifunctional antioxidants has always been a research hotspot. Many antioxidants cannot enter cells due to permeability or cellular rejection and can only scavenge extracellular free radicals, protecting the cell membrane. However, they are powerless against oxidative damage to the mitochondrial membrane, which is key to cellular aging.
In recent years, multiple studies have found that Coenzyme Q10, as a component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane's lipid bilayer, not only plays a coenzymatic role in cellular energy production but also protects against free radical attacks on the mitochondrial membrane. Therefore, this article starts by introducing Coenzyme Q10 and then details its miraculous antioxidant effects.

Introduction to Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10, also known as ubiquinone 10, is a quinone ring compound with strong antioxidant functions, anti-aging properties, and the ability to boost human immunity. It assists in treating many cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, tumors, and more. As both a medicine and food source, it can be used in pharmaceuticals and as a food additive. When the human body has a severe deficiency, supplementation through food is essential.

Sources of Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 is widely distributed in the human body, with varying concentrations in different parts, mainly abundant in organs like the liver and heart. The body can obtain Coenzyme Q10 through two ways: self-synthesis and dietary intake. Self-synthesis requires the participation of B vitamins, pantothenic acid, and several trace elements. Insufficient synthesis can cause symptoms in the body. Therefore, dietary or medicinal supplements are necessary. Coenzyme Q10 is relatively high in foods such as fish, animal organs, beef, pork, and peanuts, but lower in milk.
As a high molecular weight compound, Coenzyme Q10 has poor water solubility and low absorption levels in the small intestine, leading to low oral bioavailability. Its stability is also challenged by environmental factors like light and heat, limiting its application as a dietary supplement in health foods.
LiposoMore encapsulates Coenzyme Q10 using innovative liposome technology, significantly improving encasement rate and stability. This not only demonstrates that liposomes effectively enhance Coenzyme Q10 solubility but also proves that liposomes are an effective means of delivering Coenzyme Q10 in a stable manner.

Coenzyme Q10 Raw Material

Liposomal Coenzyme Q10 Raw Material
In simulated in vitro digestion experiments, the micelle appearance at the endpoint of the simulated intestinal digestion experiment was examined, and the bioacceptability was calculated based on the Coenzyme Q10 content in the micelles. As shown in Figure 1, liposomal encapsulation significantly enhances the bioacceptability of Coenzyme Q10.
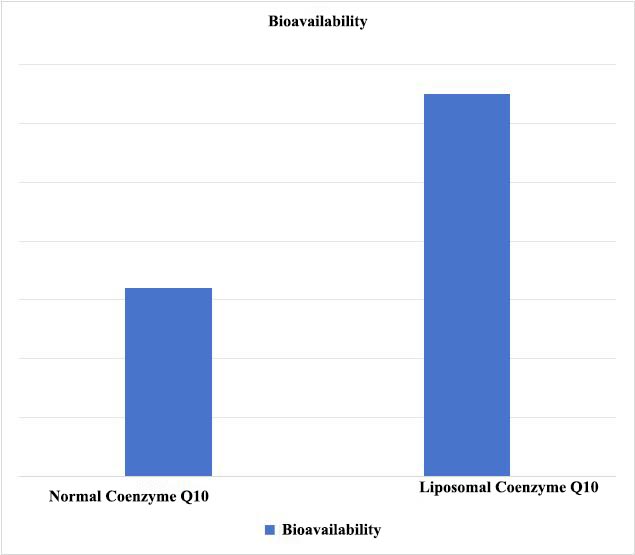
Figure 1 Bioavailability of Coenzyme Q10
To verify the antioxidant capacity and content of LiposoMore liposomal Coenzyme Q10, the DPPH method was used to measure the antioxidant capacity, and the microplate method was used to measure the content, providing a reliable basis for product quality control and efficacy evaluation.
01
Antioxidant Capacity Test Results
Experimental data show that liposomal Coenzyme Q10 has sustained antioxidant capacity: liposomal Coenzyme Q10 exhibits consistent scavenging of DPPH free radicals in a simulated intestinal environment. The scavenging rate of liposomal Coenzyme Q10 tends to stabilize with incubation time and is superior to the control group, effectively neutralizing free radicals and alleviating oxidative stress.
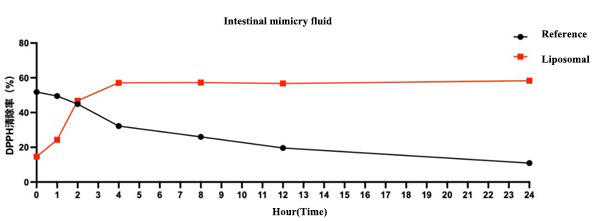
Figure 2 Different concentrations of liposomal Coenzyme Q10 scavenging DPPH free radicals after incubation in simulated intestinal fluid
02
Liposomal Coenzyme Q10 Content Measurement
Experimental data fully indicate that liposomal Coenzyme Q10 content stability is excellent: liposomal encapsulation technology can maintain the effective release and retention of Coenzyme Q10 under simulated intestinal conditions, suggesting that the liposome carrier enhances the stability and bioavailability of Coenzyme Q10.
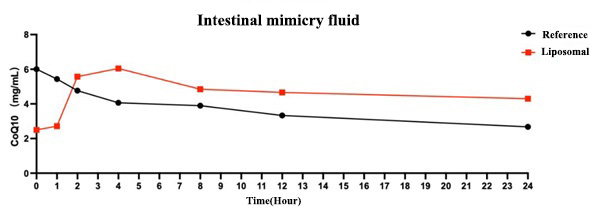
Figure 3 Coenzyme Q10 content in liposome samples after incubation in simulated intestinal fluid at different time points
The above experimental results show that LiposoMore's liposomal Coenzyme Q10 has excellent bioavailability, along with enhanced sustained antioxidant capacity and stable content.
The Dietary Nutrition and Biological Metabolism Evaluation Institute mainly researches the absorption, transformation, metabolism, and distribution of nutrients in the body. Through in vitro simulation, clinical evaluation, and AI evaluation, combined with pharmacokinetic research, it provides scientific evidence for safe, effective, and rational nutrient supplementation in clinical practice.
Natalie Wu
Hey Guys, I am Natalie Wu, an R&D researcher at LiposoMore. I graduate from College with a Master’s Degree in Bioengineering, I would like to share news and the science behind liposomal ingredients. At LiposoMore, we drive ingredient development with scientific precision and a passion for advanced nutritional technologies.

 EN
EN
 jp
jp  ko
ko  fr
fr  de
de  es
es  ru
ru  pt
pt  ar
ar  pl
pl  vi
vi 








































