2.1 High bioavailability
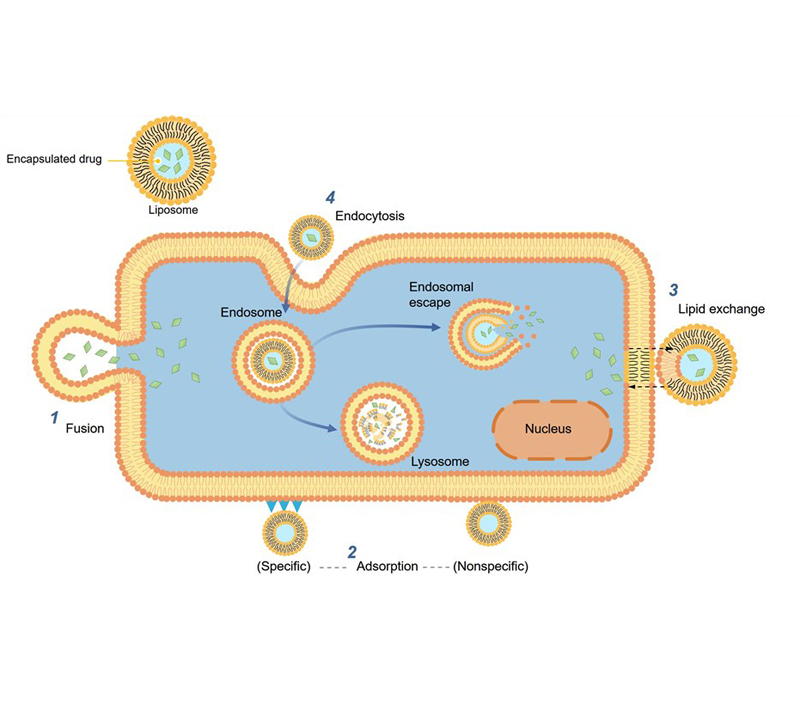
Membrane-like structure promotes absorption: Liposomes are similar to intestinal cell membranes and directly enter the circulatory system through membrane fusion or endocytosis, bypassing the loss of traditional digestive processes.
Lymphatic system absorption: Liposomes can be absorbed through intestinal lymph (chylomicron pathway), improving the transport efficiency of fat-soluble vitamin D3.
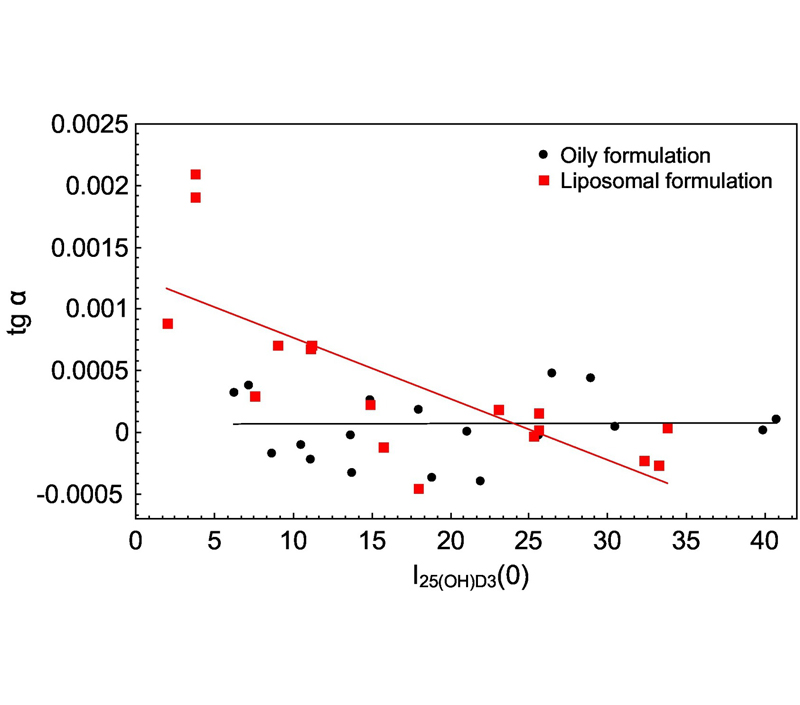
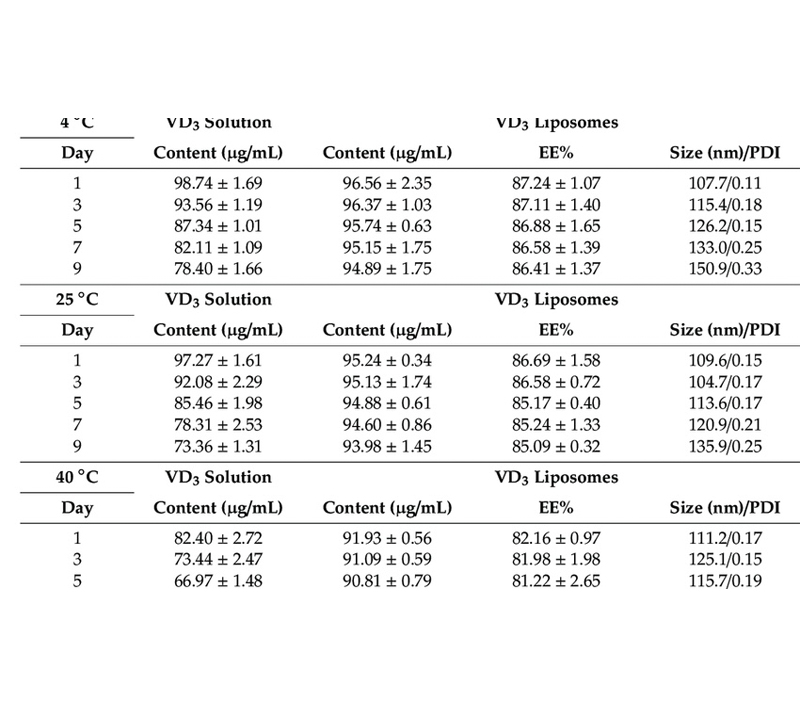
Figure 1: It has been demonstrated in a clinical experiment that liposomes Vitamin D3 are superior to oily formulation concerning their capability in delivering vitamin D3. Also, the clinical experiment shows that vitamin D3 in liposomal form was absorbed faster by persons with distinct deficiency.

 EN
EN
 jp
jp  ko
ko  fr
fr  de
de  es
es  ru
ru  pt
pt  ar
ar  pl
pl  vi
vi