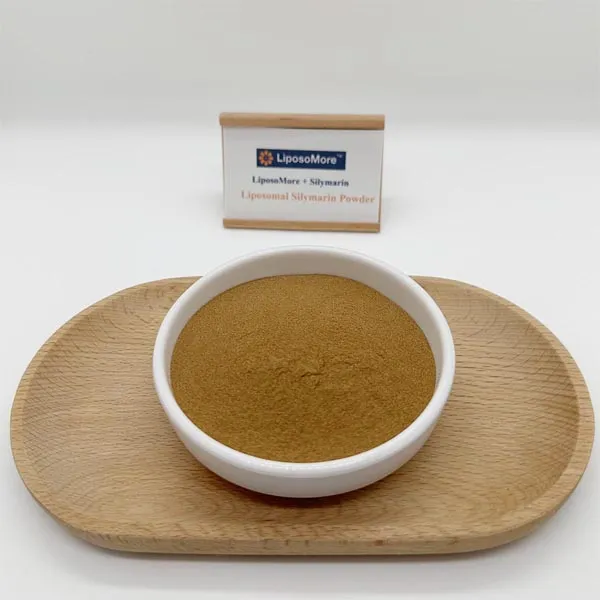
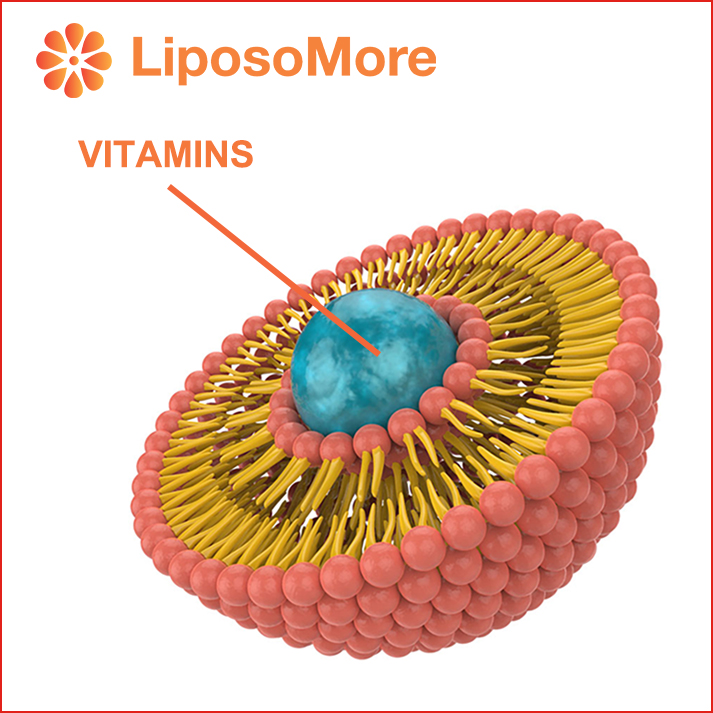
Liposomal vitamins are vitamins ingredients microencapsulated within liposomes—tiny spherical vesicles made from phospholipids, similar to cell membranes. This advanced delivery system helps protect the vitamins from degradation in the digestive tract and enhances their absorption into the bloodstream.
As a result, liposomal vitamins offer improved bioavailability compared to traditional oral supplements, making them more effective at delivering nutrients to cells.
Liposomal vitamins disperse uniformly in water-based formulations with ease, Perfectly suited for drink shots, syrups, and oral sprays.
Liposomal encapsulation protects the vitamins from oxidation and moisture damage, extending the shelf life of vitamins ingredients.

 EN
EN
 jp
jp  ko
ko  fr
fr  de
de  es
es  ru
ru  pt
pt  ar
ar  pl
pl  vi
vi